CertExams.com Simulator Lab Exercises Answers
Description: This lab exercise demonstrates configuring all three types of NAT namely Static NAT, Dynamic NAT and Overloading (Port Address Translation).
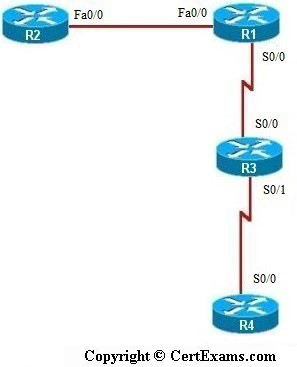
IP Address Assignment Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Mask |
| R1 | Fa0/0 S0/0 |
192.168.1.1 |
255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 |
| R2 | Fa0/0 | 192.168.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 |
| R3 | S0/0 S1/0 |
192.168.100.2 192.168.200.1 |
255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 |
| R4 | S0/0 | 192.168.200.2 | 255.255.255.0 |
Instructions:
1.
On R1, configure NAT to statically translate R2’s 192.168.1.2 Ethernet
address to 200.200.200.2
2. Telnet from R2 to R3 to
test the static NAT translation
3. Issue show users command on
R3 which should show that the device with 200.200.200.2 (Translated IP
Address) is the logged in device.
4. Issue show ip nat
translations command on R1 to display the NAT Translation table. The
response of this command should show that the inside local IP Address
(192.168.1.2) is translated to to inside global IP Address (200.200.200.2)
5. On R1, remove the
previously configured static NAT commands and configure NAT to translate
R2’s Ethernet address to a dynamically assigned address. For this,
utilize a pool of public addresses in the range of 200.200.200.50 to
200.200.200.100
6. Telnet from R2 to R3 to
test the dynamic NAT translation
7. Issue show users command on
R3 which should show that the device with 200.200.200.50 (Translated
Address) is the logged in device
8. Issue show ip nat
translations command on R1 to display the NAT Translation table
9. On R1, remove the previous
NAT commands and configure NAT Overloading (Port Address Translation) on
R1 to translate R2’s Ethernet address (192.168.1.2) to Serial 0
interface address (192.168.100.1)
10. Telnet from R2 to R3 to
test the PAT function
11. Issue show users command
on R3 which should show that the device with 192.168.100.1 (Translated
Address) is the logged in device
12. Issue show ip nat
translations command on R1 to display the NAT translation table
Note: Please refer to the CertExams.com Network Simulator software for complete lab with commands.